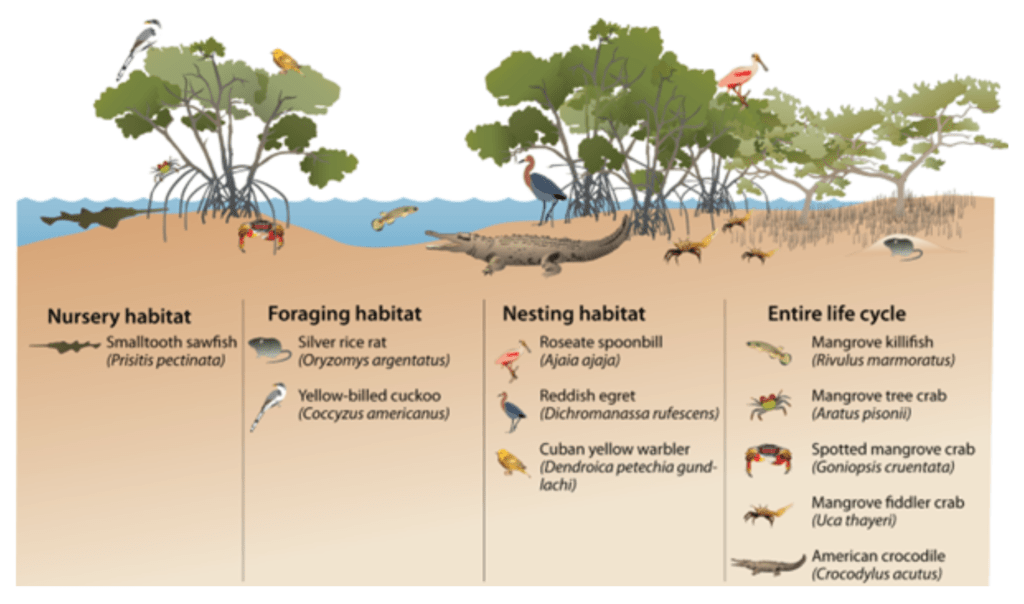
- Our Future: Solutions
- Voices of the Ocean
Diving into Kalk Bay: Exploring its past, present, future

My earliest, enduring memory of the Ocean is a stretch of sea rolling away from a vibrant fishing harbour in Kalk Bay, Cape Town.
The harbour’s position along the False Bay Coast, as well as its rich marine life, played a crucial role in the city’s early development and prosperity. Little did I know this place would also play an important role in my own life.
Kalk Bay: A link to my childhood and the last connection to my grandmother.
The colourful fishing boats in the harbour that frame the glorious, shimmering stretch of Ocean in my mind like a postcard, idealised to a point far from reality. Today, with names like Star of the Sea and Lucky Strike, those old wooden boats seem struck in a rapidly receding past.
Change has come in great variety and moved with incredible momentum. All aspects of the scene have been altered – from the oceanography and to the social structures and human dimension surrounding the harbour.
I find it interesting and unsurprising, that when asked to think of a memory about the Ocean, the one I recall is so entangled with the influence of mankind. These two elements – human and Ocean – have been linked for centuries and seem unable to escape one another.

I feel this tension reflected in the complex and often contradictory nature of our social and ecological aims moving forwards as a society.
Progression too often comes at the high cost of our marine health, a lack of respect for our past and insufficient foresight for our future. All of this points to the difficulty in honouring and preserving our collective pasts whilst building future horizons in sustainable ways.
New strategies for managing the natural environment and its resources should include integrated approaches with new frameworks, stakeholders and communities.
Kalk Bay as we see it today
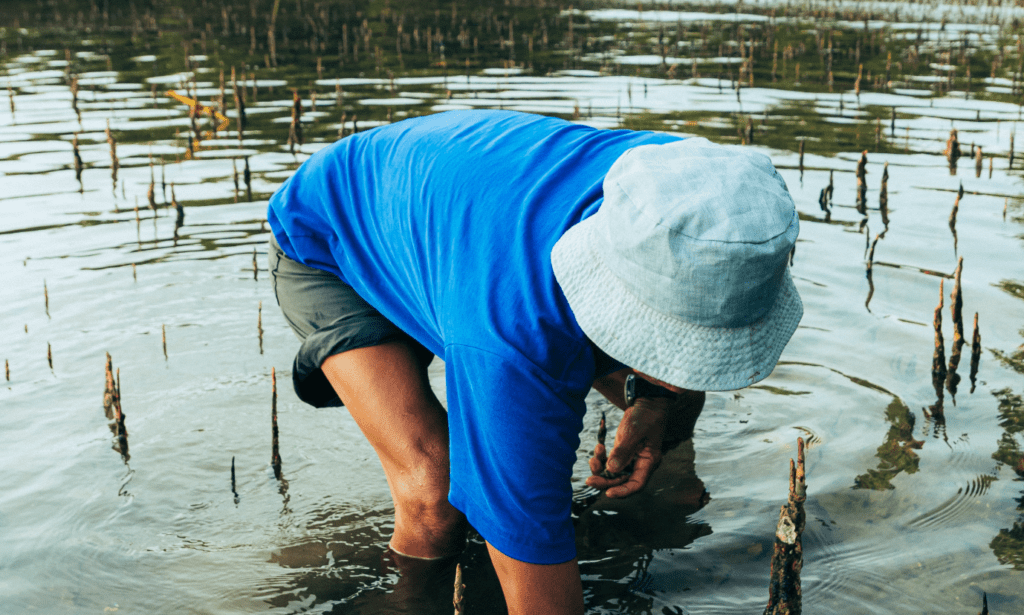
The Kalk Bay area may be reminiscent of the past, but the issues it faces are very much of the present. The harbour is one of the few still in operation, albeit a far cry from its thriving commercial days. Subsistence fishing (the practice of catching fish for personal consumption and not profit) is carried out with a handful of crayfish boats heading out each day.
With reduced operation has come tourism and commercialisation. You will find restaurants, pop up stalls selling gimmicks, and seals, who emboldened and adjusted to the crowds, sunbathe on the jetty.

Just as the Ocean below has been altered by rising sea levels and an increased frequency of extreme temperature events, so too has the harbour. Unsurprisingly, the advancements and demands of modern life have been the indirect driving forces behind this change.
All the usual culprits – overfishing, climate change, overpopulation, and coastal development- are part of this problem. Fish stocks caused by overfishing and the violations of size regulations have impacted marine biodiversity and the livelihoods of local fisherman.
Coastal development have also contributed significantly to these detrimental changes by increasing pollutant runoff and nutrient loading.
This illustrates just how interrelated Ocean and coastal ecosystems are and how integral they are to both human and aquatic life.

Not all hope is lost for Kalk Bay
Thankfully, there’s been a growing awareness of and respect for some of these pressing human-made threats, which has led to the establishment of marine protected areas. Currently, 15 % of South Africa’s total marine areas are protected with 1.7 % of this area fully protected.
Evidently, the South African constitution recognises the need for these conservation efforts and acknowledges the responsibility that the fishing and tourism industries have.
Eco-tourism has emerged as a way of protecting and sustainably using the environment, without negatively impacting economic growth and job security.

We need solutions that engage local communities living in coastal areas. This would encourage the safeguarding of natural resources, improve the quality of people’s lives, and potentially assist in building bridges between sections of South African society that has historically been divided.
Approaches such as these work towards achieving a balance between developmental goals and environmental concerns; it’s of course an ongoing process. Therefore, it’s important to thoroughly research and address the priorities and gaps in this area with input from various stakeholders.

My grandmother’s childhood saw the days when man could still outrun his actions without stopping to catch his breath and consider any of the implications. The harmony between human and Ocean that existed was only ever on a short-term loan, one with dangerously high interest.
The future seemed as it always does to those on the shores of the present: An island far away.
![Katie, a Wavemaker shares this quote: My faith in the [...] next generation of changemakers gives me hope for the future of our marine and coastal ecosystems.](https://oceangeneration.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/next-generation-of-changemakers-gives-hope-for-marine-ecosystems-1024x604.jpg)
The generation of young people to which I belong to understand that preservation isn’t about merely respecting the present but also about securing the future. Therefore, my faith in the collective creativity and problem-solving abilities of the next generation of changemakers gives me hope for the future of our marine and coastal ecosystems.
Thank you for raising your voice for the Ocean, Katie!
Connect with Katie Birditt via LinkedIn or her Instagram page. Learn about how to submit your own Wavemaker Story here.
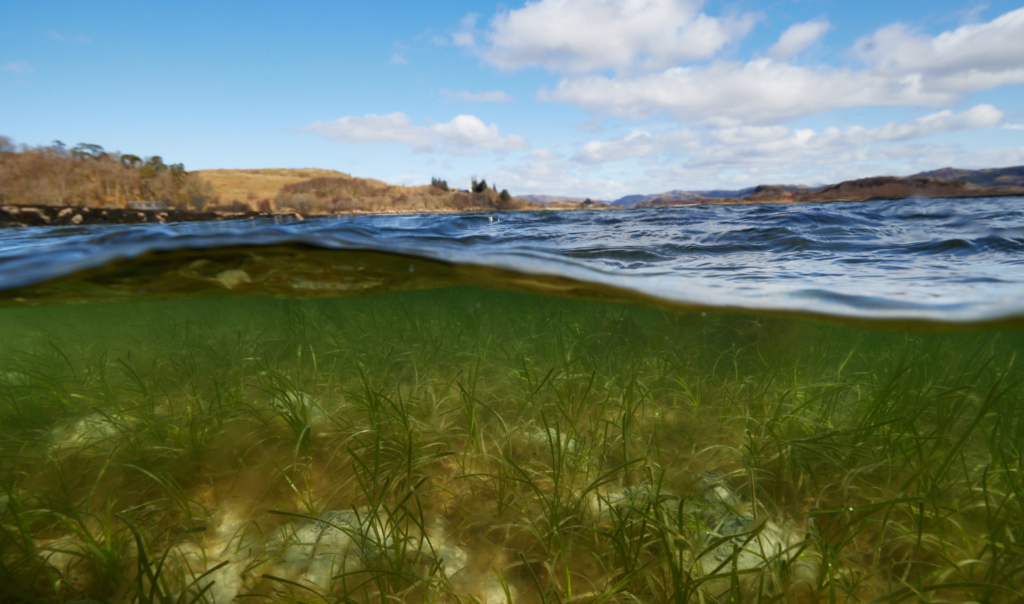





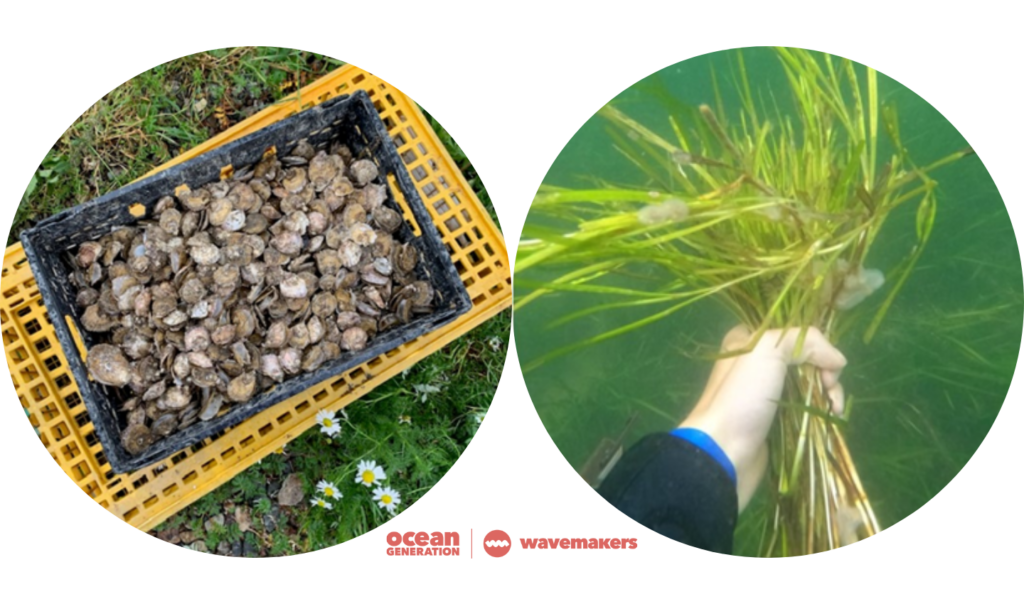
![Woman diving into the Ocean shared by Ocean Generation in a Wavemaker Story. There's a quote that reads: I spent my summer [...] restoring seagrass meadows and native oyster reefs. Photo by Sophie Coxton.](https://oceangeneration.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/community-led-marine-habitat-restoration-organisation-Scotland-restore-seagrass-meadows-and-native-oyster-reefs-1024x604.jpg)






























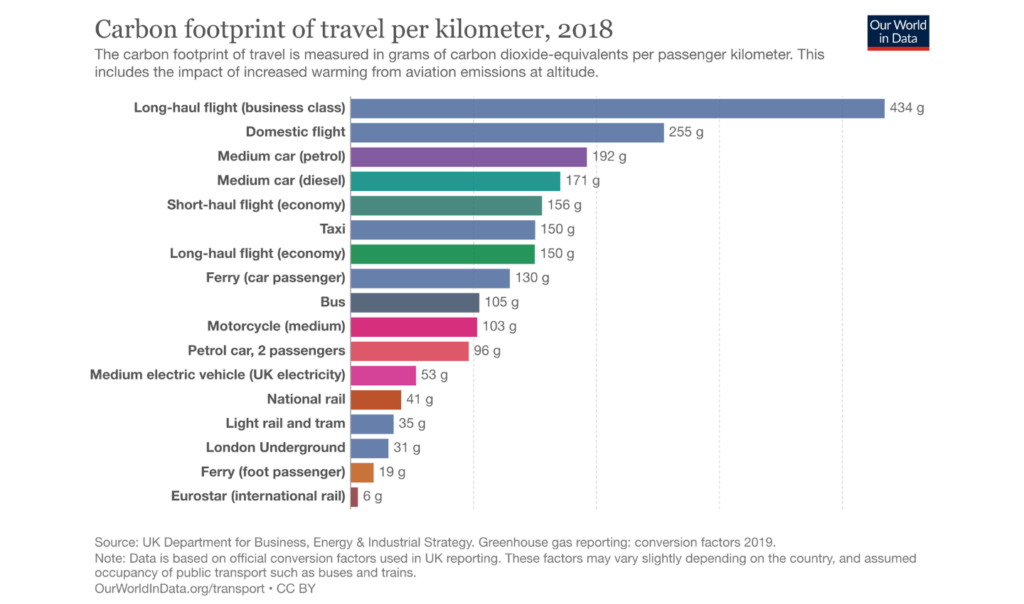










![Greenhouse gas emissions across the supply chain for 8 different types of food. [Credit: Our World in Data]](https://oceangeneration.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/food-type-greenhouse-gas-emissions-across-supply-chain-Generation-1024x604.png)
![Greenhouse gas emissions across the supply chain for 8 types of food. [Credit: Our World in Data]](https://oceangeneration.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/food-greenhouse-gas-emissions-across-supply-chain-Generation-1024x604.png)