- Our Impact: Threats
- Science: Explained
- Take Action
15 Plastic Pollution Facts You Should Know
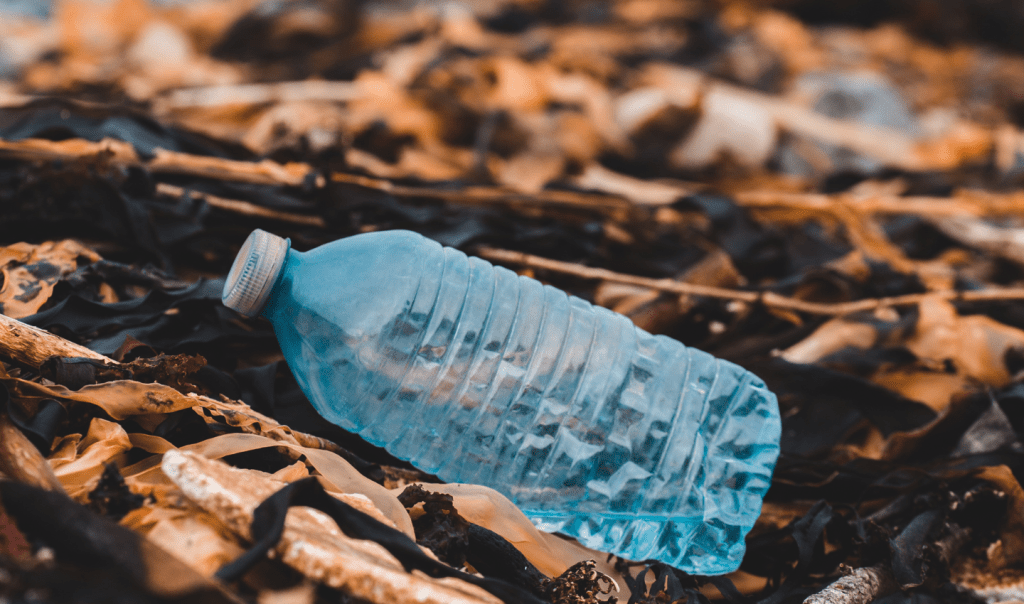

We’ve become dependent on single-use plastic products.
And the reason why isn’t hard to find. Plastic is cheap, convenient and was made to last forever – but as plastic pollution has severe environmental and health consequences for our blue planet.
Understanding key facts about plastic pollution is the first step to rethinking our relationship with it, and ensuring a healthier, more sustainable future all life on Earth.
We’re breaking down 15 facts about plastic pollution – backed by science and our expertise as experts in Ocean health since 2009. Find out how plastic enters the environment, its impact on wildlife, what microplastics are, and how it effects our health below.
15 Plastic pollution facts you need to know:
1. Up to 422 million tonnes of plastic are being produced each year.
The amount of plastic produced every year weighs more than all of humanity (estimated at 316 million tonnes in 2013).
2. Up to 12.7 million tonnes of plastic enter the Ocean every year.
If waste management practices don’t improve, scientists predict this amount could increase tenfold by 2025.
Single-use plastic items are the biggest contributors to marine litter (it is estimated that 1 – 5 trillion plastic bags are consumed worldwide each year).
3. Plastics make up to around 75% of marine litter, although this can be up to 100% at some sites.
Plastic in the Ocean breaks up into smaller fragments called microplastics, which have been identified in commercial fish and thus, consumed by humans.
4. Plastic in the Ocean breaks up into smaller fragments called microplastics.
Plastic will never go away. These microplastics have been identified in commercial fish consumed by humans.
What are microplastics?
Microplastics are small plastic pieces measuring less than 5 millimetres.
While some microplastics are intentionally made small (like microbeads in facial scrubs and industrial abrasives used in sandbags), others have been formed by breaking away from larger plastic products.
Due to large amounts of plastic pollution, microplastics can now be found everywhere on Earth – from Mount Everest to the Mariana Trench; the deepest part of our Ocean.
5. Half of all plastics are single-use applications, meaning they’re used just once and disposed of.
We are all guilty of using single-use plastic items. From shampoo bottles to make-up products, plastic forks, and straws – single-use plastic is part of our daily lives.
Small behaviour changes can make a massive impact in reducing the flow of plastic pollution to the Ocean.
The next time you’re at the store, reaching for a single-use plastic item, stop and consider: Is there a more sustainable product I can use? If not, think of ways you can reuse your plastic items instead of discarding of them once you’re done.
6. Plastic was invented 150 years ago.
When we see the stat, ‘Plastic takes 450 years to decompose’ we reply, ‘How is that known?’ Plastic hasn’t been around long enough for us to confirm that.
Instead of breaking down, it’s more accurate to say plastic breaks up.
Plastic is indestructible; it was designed to defy nature, and designed not to decompose. Plastic just gets smaller, making it harder to remove from the Ocean.
7. Birds are highly susceptible to plastic ingestion.
It is estimated that over 90% of all seabirds have ingested plastic.
8. There is no giant floating island of plastic at the centre of the Pacific or any other parts of the Ocean.
The so-called Great Pacific Garbage Patch is invisible from the surface.
Plankton nets, however, reveal the true nature of the plastic problem: An accumulation of microplastics that fill up each net in concentrations that increase towards the Ocean’s centre.
9. Plastic acts as a sink for chemicals in the environment, and transports them.
When plastic is mistakenly consumed by marine life, plastic chemicals are released and stored in the fatty tissue of the animal.
Those chemicals travel up the marine food chain, magnifying in concentration on their way up. Eventually, the plastic in fish reaches and gets consumed by people.

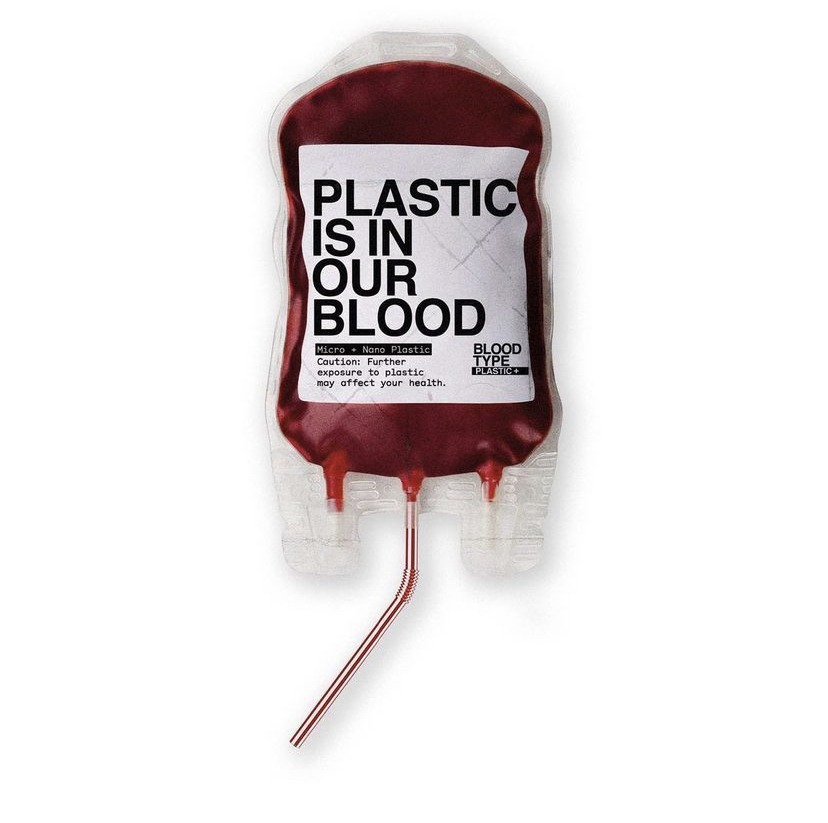
10. Chemicals are added to plastic during its production.
Chemicals are added to plastics to give the products certain properties. Some of the chemicals, known endocrine disruptors, have been linked to critical diseases including birth defects, cancer, autoimmune disease, infertility and cognitive and behavioural disorders.
So, plastic isn’t just polluting our Ocean – it’s polluting our bodies.
11. Crustaceans tested at the deepest point of our Ocean have ingested plastic.
Animals from the deepest places on our blue planet have been found with plastic in their stomachs, confirming fears that man-made fibres have contaminated the most remote places on Earth.
12. People living along rivers and coastlines are the most impacted by plastic pollution.
It’s been reported that China, Indonesia, the Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam are the most impacted by plastic pollution.
13. Low-income communities face more health impacts near plastic production sites.
Communities with low incomes have greater exposure to toxins and plastic waste, and bear the brunt of the impacts of improper plastic disposal and incineration.
14. Annual plastic production has skyrocketed since the early 1950s, reaching 322 million tonnes in 2015.
These numbers do not include synthetic fibres used in clothing, rope and other products which accounted for 61 million tonnes in 2016.
The World Economic Forum (WEF) predicts a 3.5 – 3.8% growth in plastic production per year through 2050. As of 2019, we’re seeing proof of this – with production of single-use plastics increasing despite our growing awareness of their negative impacts.
15. Bioplastics are not not as green as they seem. Approach with caution.
Though companies often market bioplastics under the same umbrella as biodegradable products, they are not necessarily biodegradable.
Most bioplastics require very specific conditions to break down effectively. They also do not solve the litter or throwaway culture problem.
What is plastic – really?
To ensure a healthy future for our Ocean and planet we must decrease our plastic dependency.